AP Initiates Carbon Market to Protect Mangrove Forest
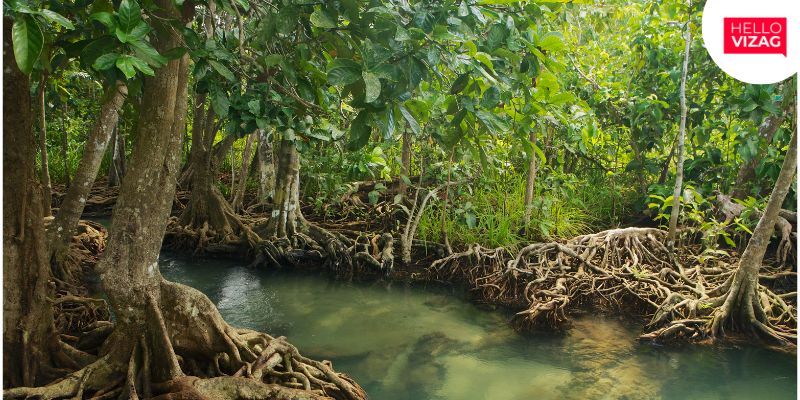
Visakhapatnam: The Andhra Pradesh Forest Department (APFD) is set to launch an innovative carbon market initiative aimed at protecting and restoring the state's vital mangrove forests.
Following a directive from the state government to explore sustainable mangrove conservation options, the APFD plans to implement a public-private partnership model. This approach will secure additional funding through the generation of carbon credits, leveraging the carbon sequestration potential of mangroves. These credits will be sourced from existing mangrove forests and new plantations under the mangrove restoration program.
Officials have identified approximately 5,360 hectares in the Krishna Wildlife Sanctuary, spanning Machilipatnam, Guntur, and Bapatla districts, for this project. The initiative aims to achieve 1,650,000 emission reductions (ERs) over the next 20 years, significantly contributing to climate change mitigation. Remote sensing technology was utilized to pinpoint suitable land for this effort. The planned afforestation, reforestation, and revegetation activities will involve planting native species to enhance local biodiversity, generating an estimated 600,000 carbon credits in the first 10 years and an additional 1,050,000 credits in the following decade.
Since 2020, APFD has focused on the artificial regeneration of mangroves. This initiative will continue over the next two decades, with future mangrove plantations also being quantified for carbon credits. The project encompasses habitat management, eco-development activities, and new interventions for afforestation, reforestation, and revegetation.
Habitat management activities will include monitoring the project area to reduce biotic pressure, desilting, weed removal, gap filling, and reintroduction of native species. Carbon markets facilitate the trade of emission units (carbon credits), represented by certificates signifying emission reductions. These credits can be traded internationally, allowing developed nations and multinational companies to offset their carbon footprints. Private organizations are increasingly collaborating with farmers, while government institutions also aim to generate and monetize these credits.
Carbon market mechanisms incentivize lower carbon pathways by raising awareness of the economic and environmental consequences of increased greenhouse gases and by placing a price on carbon emissions. These markets consist of voluntary and compliance sectors, with compliance markets established under the Kyoto Protocol of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, governed by obligatory carbon reduction regimes. Several voluntary carbon standards are available for trading in the agriculture, forestry, and other land use sectors.
For More Updates: Follow Us https://www.instagram.com/hellovizag.in/

 Team Hello Vizag
Team Hello Vizag